Learn English tenses -Future Continuous Tense
The English Tense System
The links below are to lessons for each of the 12 basic tenses.
In each lesson we look at two aspects of the tense:
- Structure: How do we make the tense?
- Use: When and why do we use the tense?
Some lessons look at additional aspects, and most of them finish with a quiz to check your understanding.
- Present Tense
- Present Continuous Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Past Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense
- Future Tense
- Future Continuous Tense
- Future Perfect Tense
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense
We use different tenses to describe the time that the verb refers to.
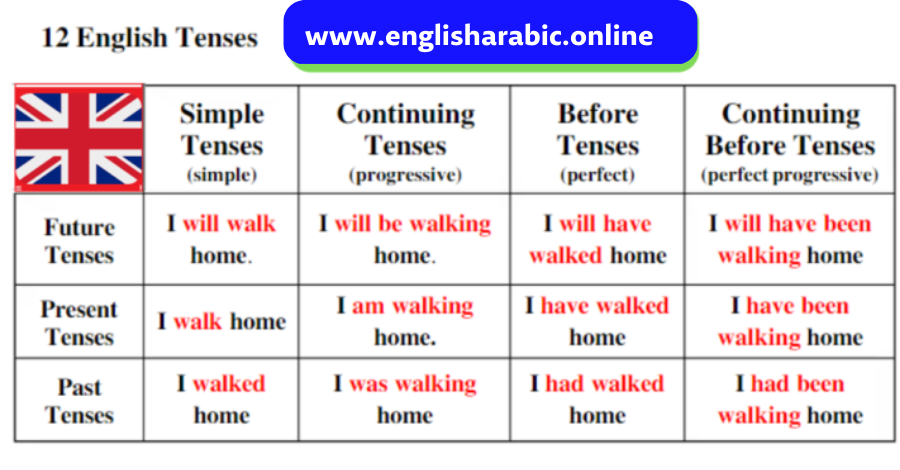
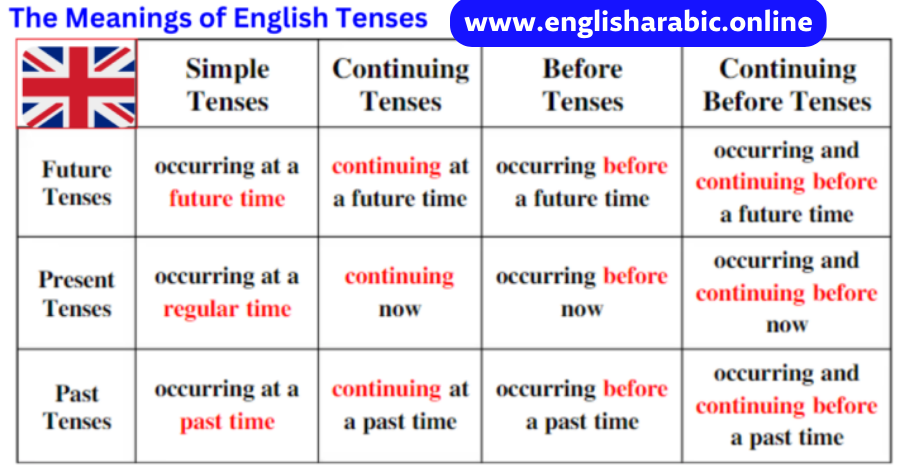
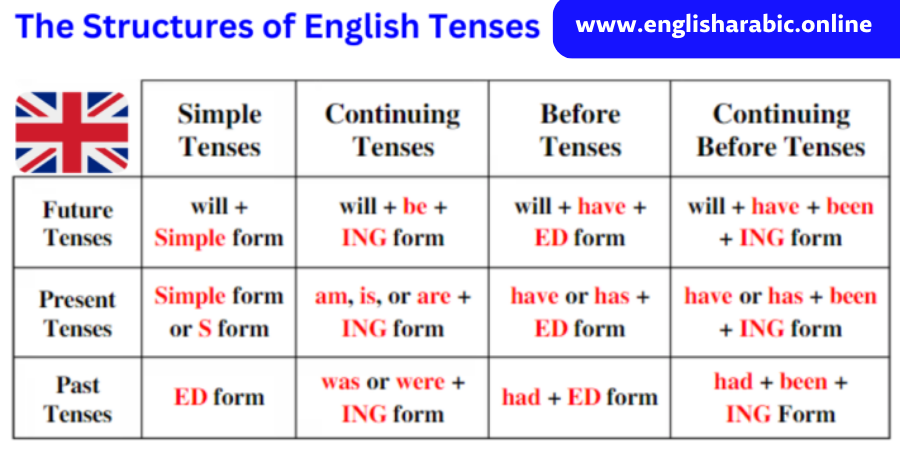
We use the future continuous tense to talk about things that will happen over a period of time in the future.
Like simple future, we can use either “will” or “going to” with the future continuous tense, but unlike simple future, there is no difference in meaning.
Note: Like all continuous tenses, you can’t use them with stative verbs, or the stative forms of mixed verbs.
Forming Future Continuous with will:
| Subject | Will | Be | Main Verb (Present
Participle) |
Rest of Sentence |
| I, you, he, she, it, we, they | will | be | driving | at 10:00 pm tonight. |
Forming Future Continuous with going to:
| Subject | Present Tense “To Be” verb | Going To | Be | Main Verb (Present Participle) | Rest of Sentence |
| I | am | going to | be | driving | at 10:00 pm tonight. |
| You, we, they | are | going to | be | driving | at 10:00 pm tonight. |
| He, she, it | is | going to | be | driving | at 10:00 pm tonight. |
Using the Future Continuous Tense
Future Events that Last a While
Use future continuous tense to talk about future events that happen over a period of time.
- When we go to Japan next summer, we will be staying with my aunt.
- I’ll be eating dinner with Janice tomorrow, so I can tell her you said, “Hello.”
- Marcel will be working in the office for the next three hours.
Future Actions that are Interrupted by Something
Use future continuous tense to talk about future actions that are interrupted by another action (the interrupting action is in a present-tense time clause)
- I’ll be driving when you call.
- Justin is going to be waiting at the station when your train arrives.
- Alice will be getting out of soccer practice when you pick her up.
Sometimes, the “interrupting” action is just a specific time. In this case, the action started before the time mentioned, and continued after the time.
- Josh will be working at midnight.
- This time next year, I will be sitting on a beach in Australia.
- By next week, Tina will be teaching medical students.
Asking Politely about the Future
You can use the question form of the future continuous tense to ask a polite, formal question about the future. If you use future simple tense, the meaning would be the same, but it would be slightly more informal and less polite.
- Will you be bringing your husband to the office party?
- Will we be sharing a room at the hotel?
- Are you going to be taking your dog on the road trip?
Ongoing Events with “Still”
Use “still” with the future continuous tense to talk about an action that has started in the present, but is expected to continue into the future.
- At 8:00 pm, I will still be cleaning my house.
- Even if we stop all carbon emissions now, the earth will still be warming up for 20 years.
- I will still be trying to understand romance when I am 90 years old.
Negative Statements
To make negative statements with the future continuous:
add “not” before “going to”
add “not” after “will.” (the most common form is “won’t”)
- I am not going to be working after 5:00 pm.
- Oliver won’t be finishing his homework any time soon.
- Sophie and Charlotte are not going to be waiting when you finally arrive.
Question Forms
Information Questions about the Subject:
To make a question about the subject of a sentence, use a question word as the subject. The form is:
question word + will + be + main verb (present participle) + rest of sentence
question word + “to be” verb + going to + main verb (present participle) + rest of sentence
- ??? is going to be traveling to Taiwan next month. –>
- Who is going to be traveling to Taiwan next month?
- ??? people will be riding on the bus. –>
- How many people will be riding on the bus?
- ???’s mother will be picking up the kids. –>
- Whose mother will be picking up the kids?
Questions about the Verb or Words after the Verb:
To make a yes/no question about the verb or words after the verb with the future continuous tense, put either the “will” or the “to be” verb before the subject:
Will + subject + be + main verb (present participle) + rest of sentence
“To be” verb + going to + main verb (present participle) + rest of sentence
- Are you going to be working late tonight?
- Will you be driving home at 6:00?
- Will Ashley be waiting for me after school?
- Is she going to be eating Thanksgiving dinner with your parents?
To make an open-ended question, put a question word (who, what, where, when, why, how) at the beginning of the sentence.
- <hr /

