Learn English tenses -Past Perfect Tense
The English Tense System
The links below are to lessons for each of the 12 basic tenses.
In each lesson we look at two aspects of the tense:
- Structure: How do we make the tense?
- Use: When and why do we use the tense?
Some lessons look at additional aspects, and most of them finish with a quiz to check your understanding.
- Present Tense
- Present Continuous Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Past Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense
- Future Tense
- Future Continuous Tense
- Future Perfect Tense
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Tenses
We use different tenses to describe the time that the verb refers to.
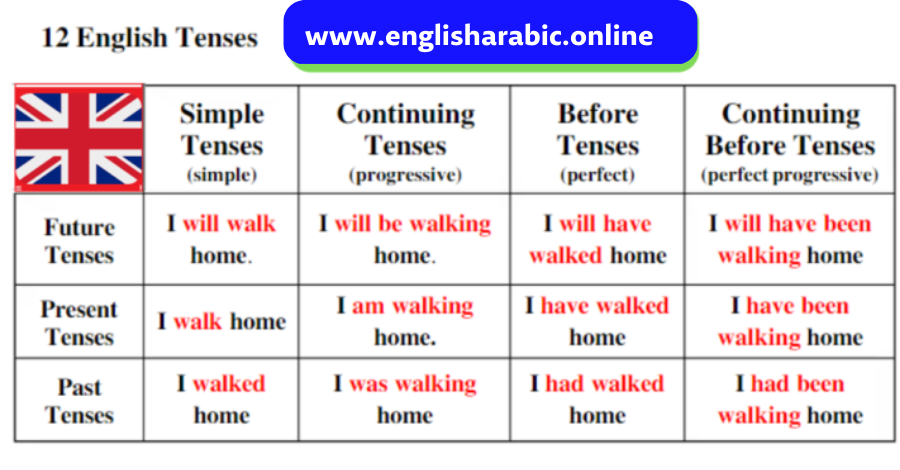
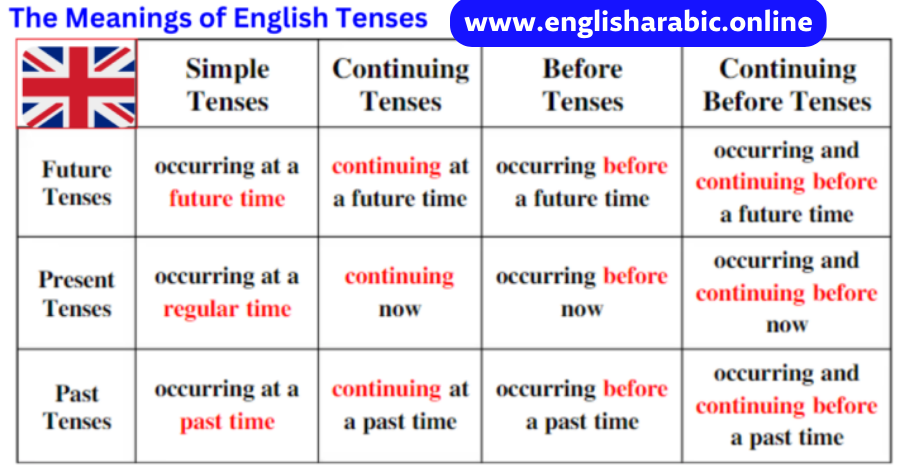
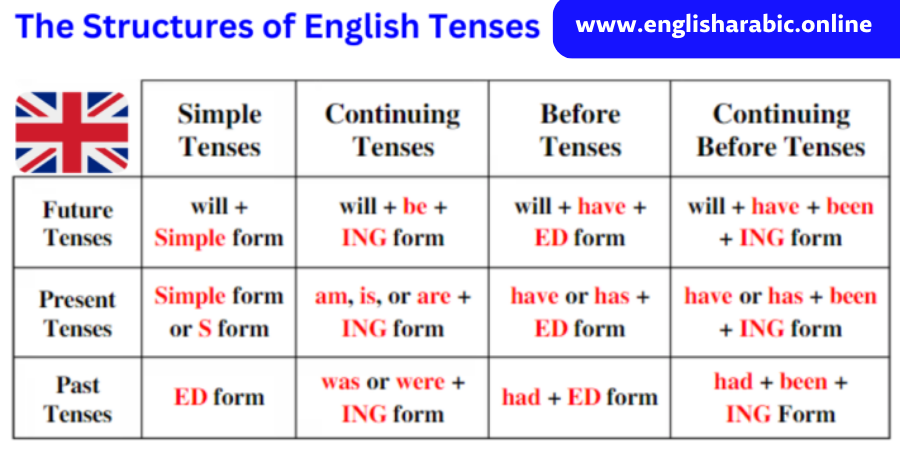
Past perfect tense
The past perfect tense is formed with had + past participle.
The past perfect tense is used most often to emphasize that one event happened before another event, and to show the relationship between them.
We form the past perfect tense by using had, followed by the main verb in past participle form.
| Subject | Had | Verb
(past participle) |
Rest of Sentence |
| I/you/we/they/he/she/it/Daniel | had | eaten | breakfast already. |
When to Use the Past Perfect Tense
A Completed Action before Another Event/Time in the Past
Use the past perfect to express that one event began and ended before another event (expressed in the past simple) in the past. It usually indicates a relationship between these two events. It can also express that something happened before a specific time in the past.
- I had already been awake for an hour when the alarm clock went off.
- By the time Oliver showed up for Thanksgiving dinner, most of his family had finished dessert.
- Hector had studied Japanese for six years before he moved to Tokyo.
Note: Sometimes you hear that “Past perfect is used when one past event happens before another past event,” but this isn’t always true. When telling a story or giving details of a past event, it’s quite common to use only simple past if the sequence of events is clear from the context. See “The Simple Past” for more details.
To Give a Reason or Explanation for Something in the Past
- The librarian scowled at Ingrid because she had not paid her late fees.
- Olivia had forgotten to buy screws at the hardware store, so she couldn’t build the shelves for her bedroom.
- Ava went to the dance with Jimmy because he had asked her first.
With Stative Verbs, to Talk about Duration up to an Event in the Past.
Stative verbs are verbs relating to internal states that aren’t used in continuous forms. Some common ones are be, exist, love, want, prefer, believe, and see, but there are many others. You can read more about stative verbs here.
You can use the past perfect with stative verbs to talk about states that started in the past and continued until another past event, described by the simple past:
- Noah had been in school for six years when he graduated.
- Sarah had always believed her marriage was perfect until her husband told her he was having an affair.
- I had never wanted to own a dog, but when my roommate brought home a pug, I changed my mind.
To Talk About “Possibilities that Never Were” with the Third Conditional
The Third Conditional Tense is used to talk about past situations that might have been different if there had been different conditions. We use the past perfect tenses to talk about the these theoretical conditions, and present perfect tenses with a modal verb to describe the result that might have occurred.
- If I had studied harder in school, I might have become a doctor.
- If we had decided to go to Spain, we would have missed my sister’s wedding.
- If you hadn’t missed your flight, we would never have met each other.
Important Note: Specific Times with the Past Perfect.
Unlike the present perfect, you CAN use specific times with the past perfect:
- Melanie had won several karate competitions in high school before she switched to Judo in college.
- Joseph had studied computer science in 1981, before the Internet became popular.
Moreover, if the past perfect actions occurred at a specific time and words like “before,” “and then,” “later,” or “after” make it clear what action happened first, you can use simple past, too, and the meaning is the same:
- Melanie won several karate competitions in high school before she switched to Judo in college.
- Joseph studied computer science in 1981, before the Internet became popular.
However, if the action of the past perfect verb did not occur at a specific time, the past perfect is necessary.
- Incorrect: I never played chess before you showed me how.
- Correct: I had never played chess before you showed me how.
- Incorrect: The play already started when we arrived at the theatre.
- Correct: The play had already started when we arrived at the theatre.
Negative Statements
The negative of past continuous is very simple –- just add “not” between the “had” and the past participle:
- Zach had not driven the car before last night.
- I had not been in Seattle long when the rain started to drive me crazy.
- Paul had not needed an alarm clock until he got a job that started at 5:00 am.
Question Forms – Past Perfect Tense
Information Questions about the Subject:
To make a question about the subject of a sentence, use a question word as the subject. the form is: question word + “had” + main verb (past participle participle) + rest of sentence:
- ??? had known this already. –>
- Who had known this already?
- ??? people had been trapped until the firemen came.–>
- How many people had been trapped until the firemen came?
- ???’s child had eaten all the birthday cake before the guests arrived.–>
- Whose child had eaten all the birthday cake before the guests arrived?
Questions about the Verb or Words after the Verb:
To make a yes/no question about the verb or words after the verb, put the “had” in front of the subject:
- Had you ever met her before that night?
- Had he always loved to solve puzzles?
- Had Grace baked the cake in time for the surprise party?
To make an open-ended question about the verb or words after the verb, put a question word (who, what, where, when, why, how) before the “to be” verb in front of the subject:
- When had you ever met before that night?
- Why had he always loved to solve puzzles?
- How had Grace baked the cake in time for the surprise party?
<hr /

